Search results
Search for "oxygen reduction" in Full Text gives 52 result(s) in Beilstein Journal of Nanotechnology.
A novel approach to pulsed laser deposition of platinum catalyst on carbon particles for use in polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2023, 14, 190–204, doi:10.3762/bjnano.14.19

- commonly used catalyst in PEMFCs is platinum on various carbon support materials, which is used in both the anode and cathode because of its high catalytic activity toward the hydrogen oxidation reaction (HOR) and oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) [6][17][18][19][21][22][23][24][25]. Pt is also characterized
- properties of the investigated catalysts. The number of electrons obtained in the oxygen reduction reaction (the number of electrons per O2 molecule) on electrodes made of the tested catalytic materials, and the resulting amount of hydrogen peroxide produced were determined based on polarization curves
- electrode. The oxygen reduction efficiency of both commercial catalysts is similar (Figure 5a, Table 2), but the catalyst HiSpec 3000 has a small advantage due to the lower percentage of hydrogen peroxide in the oxygen reduction products (Figure 5d). The fabricated catalysts of series A, B, C, and D also
Non-stoichiometric magnetite as catalyst for the photocatalytic degradation of phenol and 2,6-dibromo-4-methylphenol – a new approach in water treatment
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2022, 13, 1531–1540, doi:10.3762/bjnano.13.126

- higher than the bandgap energy generates holes and electrons, which, after moving to the catalyst surface, may participate in redox processes. In a basic medium, the photocatalytic process may proceed by oxygen reduction at the surface of the particles (electron transfer only) [37]. A similar electron
Electrocatalytic oxygen reduction activity of AgCoCu oxides on reduced graphene oxide in alkaline media
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2022, 13, 1020–1029, doi:10.3762/bjnano.13.89

- the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) in alkaline medium. Varying the Ag fraction in copper cobalt oxide has a significant influence on the ORR activity. At a ratio of 2:1:1, AgCuCo oxide NPs on rGO displayed the best values for onset potential, half-wave potential, and limiting current density (Jk) of
- environmentally friendly with zero emissions at the time of use. These systems have the ability to convert chemical energy into electric energy with the highest conversion possible [1][2]. The active electrode reactions include the hydrogen oxidation reaction (HOR) and the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR). The
- ). Oxygen reduction on smaller catalyst particles favours the two-electron pathway, dominated via active edge and corner sites, while the four-electron pathway is catalysed by larger particles [18][30]. The kinetics of oxygen reduction on the surface of the ACC-2 sample was studied via the Koutecky–Levich
Nanoarchitectonics of the cathode to improve the reversibility of Li–O2 batteries
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2022, 13, 689–698, doi:10.3762/bjnano.13.61

- containing a Li+-conductive aprotic electrolyte. In principle, electrochemical reactions between Li+ and O2 take place in the cathode to store and convert energy. During the discharge, the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) occurs at the surface of the cathode, where O2 is spontaneously reduced by Li+ coming
Sputtering onto liquids: a critical review
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2022, 13, 10–53, doi:10.3762/bjnano.13.2

The effect of cobalt on morphology, structure, and ORR activity of electrospun carbon fibre mats in aqueous alkaline environments
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2021, 12, 1173–1186, doi:10.3762/bjnano.12.87

- at high carbonisation temperatures it forms particles with diameters up to 300 nm. Free-standing, current-collector-free electrodes assembled from carbonised cobalt-decorated fibre mats display promising performance for the oxygen reduction reaction in aqueous alkaline media. High current densities
- ; oxygen reduction; Introduction As the global production of renewable energy is on the rise, demand for sustainable ways of storing this energy in times of overproduction increases [1]. Systems based on abundant, cheap materials with high energy densities are required. Alkaline aqueous metal–air
- overall performance [3]. The lack of discharge performance is attributed to the sluggish kinetics of the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) at the air cathode [4], which reduces the practical power density. Further improvements of the cathode are essential for the long-term success of metal–air batteries
Stability and activity of platinum nanoparticles in the oxygen electroreduction reaction: is size or uniformity of primary importance?
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2021, 12, 593–606, doi:10.3762/bjnano.12.49

- . Keywords: durability; electrocatalysts; morphology control; oxygen reduction reaction; platinum nanoparticles; size distribution; spatial distribution; Introduction Nowadays, low-temperature proton-exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFC) are gaining a wider application. This is due to their environmental
Self-standing heterostructured NiCx-NiFe-NC/biochar as a highly efficient cathode for lithium–oxygen batteries
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2020, 11, 1809–1821, doi:10.3762/bjnano.11.163

- carbon is a promising cathode material for lithium–oxygen batteries. Keywords: electrocatalytic performance; lithium–oxygen batteries; N-doped carbon; nickel carbide; oxygen evolution reaction (OER); oxygen reduction reaction (ORR); specific capacity; Introduction Clean and sustainable renewable energy
- , constant, on-demand, and reliable manner [3][4][5][6]. Oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) and oxygen evolution reaction (OER) play critical roles in many clean energy storage and conversion devices (e.g., hydrogen produced from water splitting via water electrolyzers, hydrogen fuel cells, and metal–air
- , both samples exhibit an oxygen reduction peak on the positive scan in O2, indicating that these materials have good catalytic activity towards ORR. Figure 5a shows that the ORR onset cell voltage of NiFe-PBA/PP-900 (2.86 V) is higher than that of NiFe-PBA/PP-700 (2.78 V), and the current density of the
One-step synthesis of carbon-supported electrocatalysts
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2020, 11, 1419–1431, doi:10.3762/bjnano.11.126

- electrochemical characteristics has been extensively studied in the literature [16][23], the unique synthesis method presented here is expected to influence both the electrochemically active surface area (ECSA), oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) mass activites and stability of the catalytically active Pt-NP, due to
Atomic layer deposition for efficient oxygen evolution reaction at Pt/Ir catalyst layers
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2020, 11, 952–959, doi:10.3762/bjnano.11.79

- intermittency of renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power [1][2][3]. The water oxidation (oxygen evolution reaction, OER) and its reverse, the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) represent the limiting half-reaction of regenerative fuel cells [4][5], of some batteries (metal–air batteries) [6][7] and
Nickel nanoparticles supported on a covalent triazine framework as electrocatalyst for oxygen evolution reaction and oxygen reduction reactions
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2020, 11, 770–781, doi:10.3762/bjnano.11.62

- method. CTF-1-600 and Ni/CTF-1-600 show high catalytic activity towards OER and a clear activity for the electrochemical oxygen reduction reaction (ORR). Ni/CTF-1-600 requires 374 mV overpotential in OER to reach 10 mA/cm2, which outperforms the benchmark RuO2 catalyst, which requires 403 mV under the
- the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) are two crucial processes, which require improvements through the design of efficient catalysts. Both OER and ORR suffer from slow kinetics of the four-electron transfer process [2][3]. Thus, highly efficient electrocatalysts with enhanced performance need to be
- ). Additionally, after accelerated durability tests of 2000 cycles, the material showed only a slight decrease in activity towards both OER and ORR, demonstrating its superior stability. Keywords: covalent triazine framework (CTF); electrocatalysis; nickel nanoparticles; oxygen evolution reaction; oxygen
Atomic-resolution imaging of rutile TiO2(110)-(1 × 2) reconstructed surface by non-contact atomic force microscopy
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2020, 11, 443–449, doi:10.3762/bjnano.11.35

- Systems Engineering, Kochi University of Technology, 185 Miyanokuchi, Tosayamada, Kami, Kochi 782-8502, Japan 10.3762/bjnano.11.35 Abstract The structure of the rutile TiO2(110)-(1 × 2) reconstructed surface is a phase induced by oxygen reduction. There is ongoing debate about the (1 × 2) reconstruction
- microscopy (STM) [10][11][12], transmission electron microscopy [13][14], and density functional theory (DFT) [15][16][17][18][19]. These studies have determined many surface properties such as structure, local defects, and adsorption sites. The (1 × 1) surface transforms to the (1 × 2) surface by oxygen
- reduction in ultra-high vacuum (UHV) [2][20]. Several structural models for the (1 × 2) surface have been proposed [10][21][22][23][24]. Onishi and Iwasawa proposed a symmetric Ti2O3 model (Figure 1a) based on STM measurements [10], while Wang et al. proposed an asymmetric Ti2O3 model (Figure 1b) similar to
Electrochemically derived functionalized graphene for bulk production of hydrogen peroxide
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2020, 11, 432–442, doi:10.3762/bjnano.11.34

- gaining tremendous attention due to its importance in many fields, including water treatment technologies. Oxidized graphitic carbon-based materials have been recently proposed as an alternative to metal-based catalysts in the electrochemical oxygen reduction reaction (ORR), and in this work we unravel
- method opens a new scheme for the single-step large-scale production of functionalized carbon-based catalysts (yield ≈45% by weight) that have varying functionalities and can deliver peroxide via the electrochemical ORR process. Keywords: electrochemical oxygen reduction; functionalized carbon
- Figure 3. The electrodes exhibit capacitive (double layer) behavior in N2-saturated electrolyte, while a sharp reduction peak corresponding to oxygen reduction in O2-saturated electrolyte is shown in all the cases. The intensity of the peak (peak current density) corresponds to the ORR process and varies
Synthesis of amorphous and graphitized porous nitrogen-doped carbon spheres as oxygen reduction reaction catalysts
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2020, 11, 1–15, doi:10.3762/bjnano.11.1

- Abstract Amorphous and graphitized nitrogen-doped (N-doped) carbon spheres are investigated as structurally well-defined model systems to gain a deeper understanding of the relationship between synthesis, structure, and their activity in the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR). N-doped carbon spheres were
- microporosity of the materials is critical for an efficient ORR. Keywords: amorphous carbon; graphitized carbon; hydrothermal carbonization; nitridation; nitrogen doping; oxygen reduction reaction (ORR); porosity; Introduction Fuel cells and metal–air batteries are important renewable energy technologies
- . Both rely on the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR). The best established ORR catalysts are so far based on Pt nanoparticles or Pt alloys. However, Pt is expensive and its stability under fuel-cell working conditions is limited. Therefore, alternative catalysts based on noble-metal-free, less expensive
Antimony deposition onto Au(111) and insertion of Mg
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 2541–2552, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.245

- and some superimposed negative current may be due to oxygen reduction, which starts at ≈0.36 V vs RHE (or −0.54 V vs Pt/PtO) on the Au electrode in 0.5 M H2SO4 [27]. The bulk deposition peak is much sharper because of the different diffusion behaviors in the small volume STM cell, which somewhat
Synthesis of P- and N-doped carbon catalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction via controlled phosphoric acid treatment of folic acid
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 1497–1510, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.148

- oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) at the cathode of a fuel cell. Precursors obtained by heating FA in the presence of phosphoric acid at temperatures of 400–1000 °C were further annealed at 1000 °C to afford PN-doped carbon materials. The extent of precursor P doping was maximized at 700 °C, and the use of
- acid; oxygen reduction reaction; phosphoric acid treatment; PN-doped carbon catalysts; polymer electrolyte fuel cells; Introduction The widespread application of fuel cells as clean energy sources is the most desirable way of realizing a low-CO2-emission society. In conventional polymer electrolyte
- fuel cells (PEFCs), both anode and cathode reactions are catalyzed by Pt. Compared to the anode reaction, the cathode reaction, namely the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR), is rather slow and hence requires the use of larger amounts of Pt [1], which increases the cost of PEFCs and prevents their wide
Hierarchically structured 3D carbon nanotube electrodes for electrocatalytic applications
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 1475–1487, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.146

- series resistance to promote electron transfer. CNT–CNT composites have been successfully employed as catalyst supports. Kundu et al. reported that Pt supported on such hierarchical structures showed enhanced surface atomic concentration, indicating an improved Pt dispersion. The oxygen reduction
- oxygen reduction reaction. Although there are differences in electrode preparation (in the present case, Pt is electrodeposited onto the carbon-based electrodes, probably leading to defect-rich particles (see also below), while in [52], Pt deposition has been deposited by CVD), we think that generally
Warped graphitic layers generated by oxidation of fullerene extraction residue and its oxygen reduction catalytic activity
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 1391–1400, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.137

- Abstract Carbon-based oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) catalysts are regarded as a promising candidate to replace the currently used Pt catalyst in polymer electrolyte fuel cells (PEFCs); however, the active sites remain under discussion. We predicted that warped graphitic layers (WGLs) are responsible for
- maximum specific ORR activity after 1 h of oxidation time. WGLs were found to lower the heat of adsorption for O2 and to increase the occurrence of heterogeneous electron transfer. Keywords: carbon alloy catalysts; fullerene extraction residue; oxygen reduction reaction (ORR); polymer electrolyte fuel
- ) Heat of O2-adsorption measured with a dynamic adsorption method using differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). (a) Cyclic voltammograms of the samples for the redox reaction ferricyanide/ferrocyanide (potential sweep rate = 5 mV/s). (b) Dependence of ΔEP on treatment time. (a) Oxygen reduction reaction
Multicomponent bionanocomposites based on clay nanoarchitectures for electrochemical devices
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 1303–1315, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.129

- -circuit potential (OCP) of the cell at pH 5.5 was 0.442 V, while at pH 7 the OCP was 0.298 V. This finding can be correlated to the combination of effects such as a more suitable working pH value for glucose oxidase (the optimal working pH value of GOx is close to 5) and a faster oxygen reduction at the
Alloyed Pt3M (M = Co, Ni) nanoparticles supported on S- and N-doped carbon nanotubes for the oxygen reduction reaction
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 1251–1269, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.125

- ) alloyed nanoparticles that have a very homogeneous size distribution (in spite of the high metal loading of ≈40 wt % Pt), using an ionic liquid as a stabilizer. The electrochemical surface area, the activity for the oxygen reduction reaction and the amount of H2O2 generated during the oxygen reduction
- ; nickel; oxygen reduction reaction; platinum; proton exchange membrane fuel cell (PEMFC); Introduction Proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs) convert chemical energy from the hydrogen oxidation reaction (HOR) and the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) into electrical energy. PEMFCs are one of the most
- /RHE the fractions of H2O2 produced are below 1% for all catalysts. In this voltage region, the ORR occurs only through the four electron process. The H2O2 production is significantly higher at low potential, between 0.05 and 0.4 V/RHE, because of the oxygen reduction on carbon [80]. The amount of H2O2
Glucose-derived carbon materials with tailored properties as electrocatalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 1089–1102, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.109

- -doped biomass-derived carbon materials were prepared by hydrothermal carbonization of glucose, and their textural and chemical properties were subsequently tailored to achieve materials with enhanced electrochemical performance towards the oxygen reduction reaction. Carbonization and physical activation
- of the nitrogen functionalities. Keywords: electrocatalysts; microporosity; nitrogen-doped carbon materials; oxygen reduction reaction; surface chemistry; Introduction Due to the recent increase in interest for more sustainable, renewable and cheaper energy, multiple conversion devices are being
- engines, as they are able to function as long as there is fuel, and for batteries, as they have similar characteristics under load conditions [1]. The performance of a fuel cell is mainly controlled by the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) that takes place at the cathode [2], specifically by the
Hydrothermal-derived carbon as a stabilizing matrix for improved cycling performance of silicon-based anodes for lithium-ion full cells
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 2381–2395, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.223

- nanospheres was also reported by Xia et al. [62] during the synthesis of carbon spheres containing electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction reactions. Heckmann et al. [63] investigated the use of high-temperature-treated hydrothermal carbon spheres as cathode materials for dual-ion cells and found spherical
Metal-free catalysis based on nitrogen-doped carbon nanomaterials: a photoelectron spectroscopy point of view
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 2015–2031, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.191

- ; photoelectron spectroscopy; Introduction Catalytic processes are the basis of many important technologies in the chemical industry and for energy generation, especially in the context of renewable, clean and sustainable energy production [1]. The oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) and the electrocatalytic
- techniques, engineering and synthesis of the catalyst are to be optimized to yield an optimum concentration of active sites without inactive components. RRDE voltammograms for oxygen reduction in air-saturated 0.1 M KOH at the Pt–C/GC (curve 1), VA-CCNT/GC (curve 2), and VA-NCNT (curve 3) electrodes
Synthesis of rare-earth metal and rare-earth metal-fluoride nanoparticles in ionic liquids and propylene carbonate
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 1881–1894, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.180
- [23]. Rare-earth metal containing intermetallic nano-phases have been suggested as novel materials for various catalytic applications [24]. For example, Pt3Y and Pt5Gd were predicted to be more active as Pt in the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) [25]. Nevertheless, the high reduction potentials of
Cyclodextrin inhibits zinc corrosion by destabilizing point defect formation in the oxide layer
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 936–944, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.86
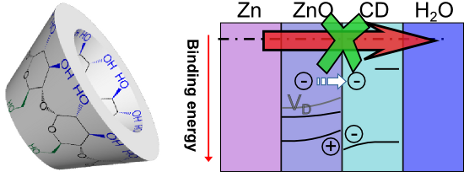
- tens of millivolts of the initial Ecorr in the presence of β-CD in the electrolyte. Lower values of Ecorr are an indication of a suppression of the cathodic process of oxygen reduction [16], Ecorr stablized quickly in the presence of the inhibitor, while reference measurements showed a slower decrease
- inhibition of the oxygen reduction and the concomitant shift in Ecorr leads to a significant decrease of the anodic dissolution, β-CD thus acts as a mixed corrosion inhibitor. It must be stressed that due to the difference in conditions –stagnant vs flowing electrolyte, chloride concentration– compared to









































































































































































































































